What is HBA?
A Host Bus Adapter (HBA) is a circuit board or integrated circuit adapter that provides physical connectivity and input/output processing between a host system (such as a server or computer) and storage devices (Hard Drive/SSD).

Two Different types of HBA
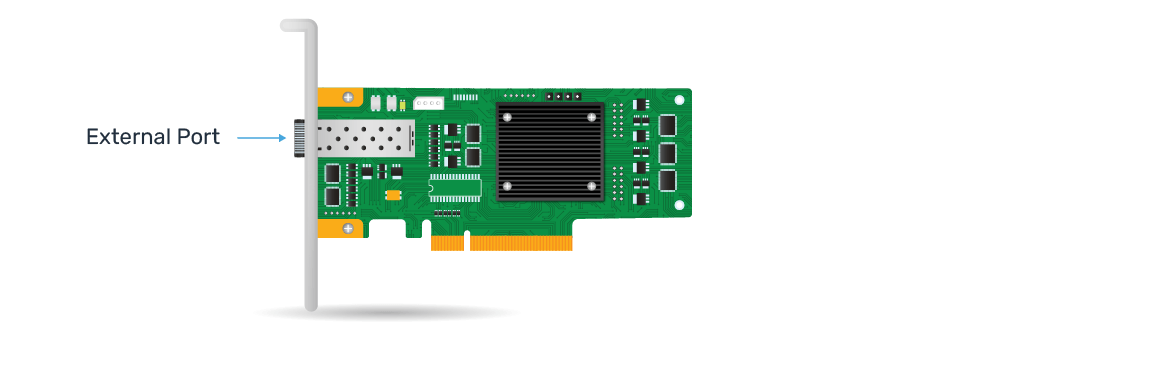
- External Port
Have ports on the outside of the computer case. They are used to connect external storage devices,
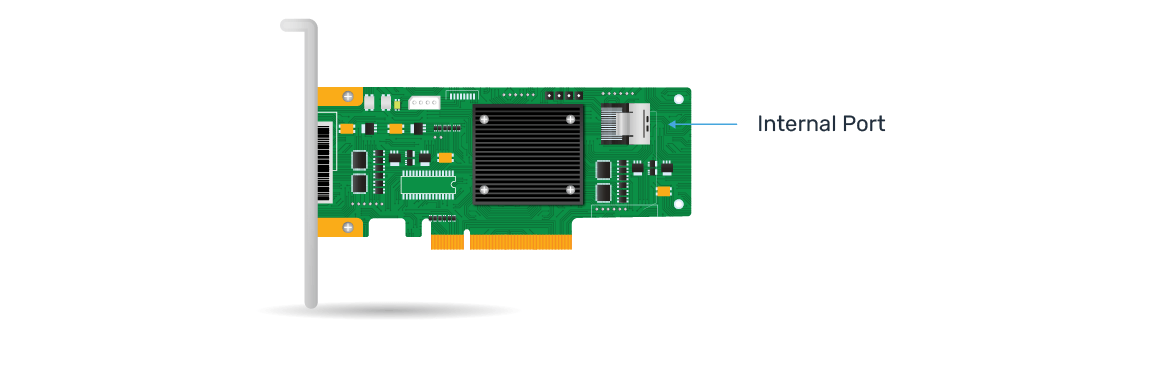
such as external hard drives, tape drives, or storage area networks (SANs). - Internal Port
Are designed to connect to storage devices inside the computer chassis. Internal HBAs are used to
connect internal storage devices like hard drives and SSDs that are mounted inside the computer case.
How HBA Works?
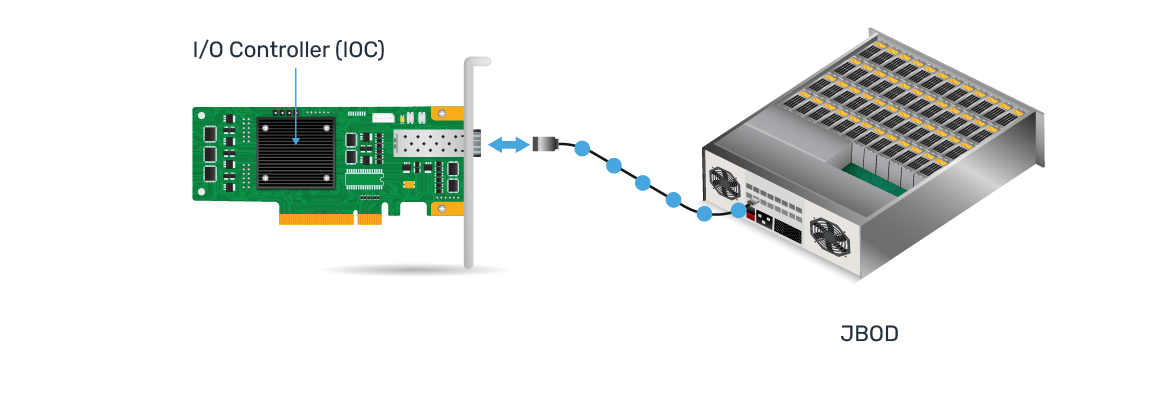
- Physical Connection - HBA is physically installed in the host system and typically connects to the system's PCI Express (PCIe) or other expansion slots to provide connection between a host computer and compatible devices.
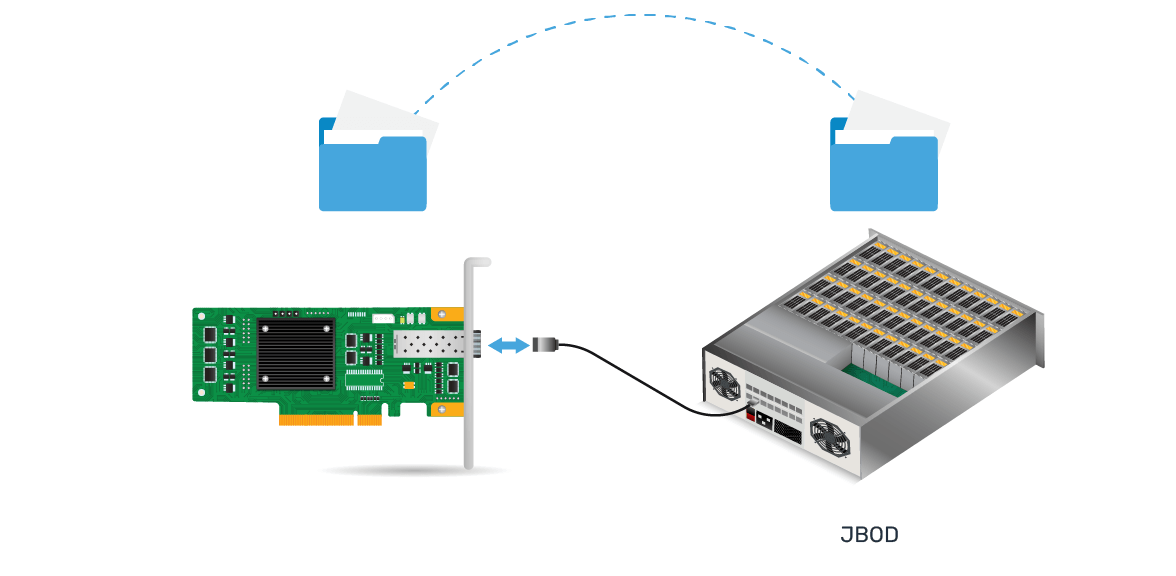
- Perform Input/Output processing - The HBA converts the data and command signals from the host system into a format that is understood by the storage devices.
- Data Transfer - HBA manages the flow of data between the host and storage devices (Hard Drive/SSD), ensuring efficient and reliable data transfer.
- Release the host computer's resources by performing data storage and retrieval operations independently.
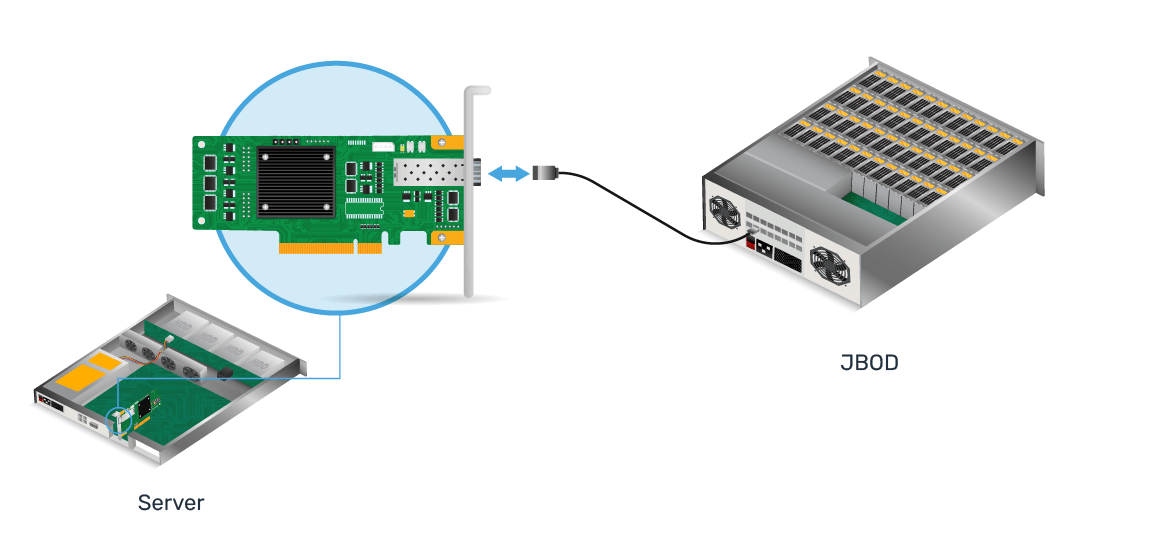
External HBA Illustration
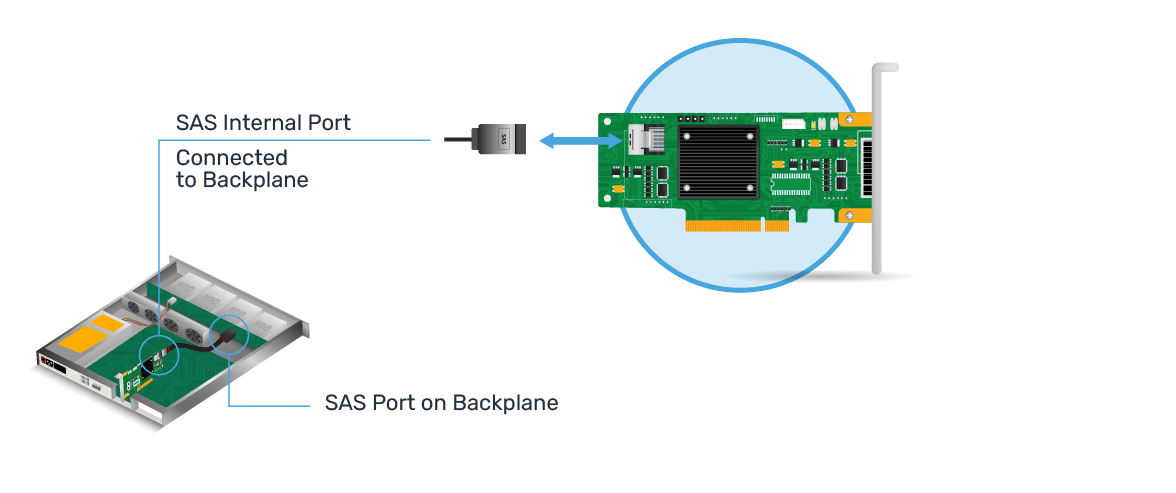
Internal HBA Illustration
Network Protocols supported by HBA
- Serial ATA (SATA) devices
- Fiber Channels
- SCSI (Small Computer Systems Interface)
HBA controllers pass the I/O command directly to the storage devices (Hard Drive/SSD), there’s no need to do caching on the HBA controller, and you will often see these cards without DRAM chips. because there’s no cache, this simplifies the hardware because it doesn’t require a power loss protection mechanism to protect volatile cache during a power loss event.
In summary, an HBA is a crucial component in enterprise-level storage systems, enabling high-speed and reliable communication between host systems and storage devices (Hard Drive/SSD), which is essential for data-intensive applications and large-scale storage infrastructures.
