Published on: January 13, 2025 | 5 minute read | by Krisa Cortez
SONiC, which stands for Software for Open Networking in the Cloud, has a rich history of evolution into a leading open-source network operating system or NOS. It was originally developed by Microsoft and was designed to run on a variety of Dell network switches and other vendor hardware, providing flexibility for users in cloud and data centers. Dell switches transitioning to using SONiC OS marked a momentous step towards furthering the use of this open source network operating system.
In Part 1 of this series, we catch a glimpse of this game-changing project, and revisit its beginnings leading up to the current driving force that it has become for many deployed systems today.
The Origins of SONiC and Its Early Stages of Development
The project began in 2016 when Microsoft identified the need for a modern, open-source network operating system that can allow a more flexible and less proprietary networking environment within its data centers. The core goal was to separate switch operating system software from hardware. This separation allowed for greater freedom in deploying various equipment from different vendors. In this framework, SONiC was created to operate on switches and Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), regardless of the manufacturer.
Transitioning to Open Source
In 2022, Microsoft transitioned SONiC to the Linux Foundation so it could become a more community-driven open source network operating system project. This shift aimed to enhance collaboration and innovation by leveraging a larger ecosystem of contributors beyond Microsoft itself. By 2024, the project had gained substantial traction, with contributions from over 4,250 members across more than 520 organizations.
Dell Switches and their Initial Exploration and Adoption of the SONiC OS
Dell began its exploration of the SONiC OS whilst seeking more open source network switch platforms. This initiative was mainly driven by a desire to provide greater usability for Dell switches and reduce costs compared to traditional systems. On account of budget constraints for hardware, Dell sought to test its Dell network switch models equipped with SONiC OS. This was where their partnership began to flourish.
Dell’s Commercially Supported Distribution
In May 2020, Dell announced a commercially-supported version of the SONiC OS, formalizing its engagement with the platform. The company introduced the "Enterprise SONiC Distribution by Dell Technologies," bringing the benefits of the SONiC open source project to enterprises looking for reliable and scalable networking solutions. This distribution is aimed at serving the wide-ranging needs of enterprise customers while allowing for the integration of Dell switch series hardware with the SONiC OS architecture.
Dell’s Other Contributions to the SONiC Project
Dell has actively contributed to the SONiC open source network software project since its inception, enhancing its capabilities and utility, particularly for enterprises. As one of the largest contributors to SONiC, Dell has focused on usability improvements and the introduction of features catering to enterprise requirements. Examples include better management tools such as the Dell switch manager, support for wide-scale deployments, among other tools. Ongoing collaboration with the open source network operating system community fosters innovation while enabling Dell to adapt its solutions to emerging challenges.
Conclusion: SONiC’s Growth, Future, and Why It’s Still the Best OS for Switches
As of this year, 2025, SONiC continues to develop its capabilities and expand its functionality in the enterprise edge market. Its ever-evolving aim is to adapt to the constantly changing needs of modern networking. The growth in its user base and support reflects an increased recognition of its value in providing flexible and cost-effective networking solutions even for the most complex of infrastructures.
SONiC’s transformation from a proprietary Microsoft project to a collaborative open source network operating system platform exemplifies the potential of community-driven innovations in networking technology. Collaboration with hardware vendors like Arista Networks, Edgecore, and Mellanox (now part of NVIDIA) enables SONiC to continually grow. Aside from Dell and Microsoft, SONiC has garnered significant collaborations with other manufacturers, advancing its effectiveness and reach within the networking landscape.
Furthermore, retaining its FREE status allowing for anyone to build upon, centered on a more community-driven approach, fosters engagement with various other networking organizations. This places the SONiC Operating System at the forefront of open-networking innovation every time.
You Ask. We Answer!
Question: What is in SONiC’s architecture that makes it beneficial for networking?
Answer: SONiC is built on a microservice-based architecture using what we call “containerization”. This design allows different networking functions to run independently within Docker containers. The separation grants operators greater flexibility to manage and update individual components without affecting the entire system.
Question: What role does Dell Technologies play in the continuous development of SONiC?
Answer: Dell Technologies is actually one of the largest contributors to the SONiC project and provides essential features and support aimed at enterprise needs. This includes management frameworks, security features, and CLI (Command Line Interface) enhancements. All while also ensuring its hardware integrates smoothly with SONiC.
Question: Can SONiC be utilized in environments other than data centers?
Answer: Yes. SONiC has been adapted for use in various environments beyond data centers. We shall discuss this as well as successful company case use examples in further detail in one of our other articles in this Series
Question: How does the ‘Enterprise SONiC Distribution’ offered by Dell differ from the standard SONiC?
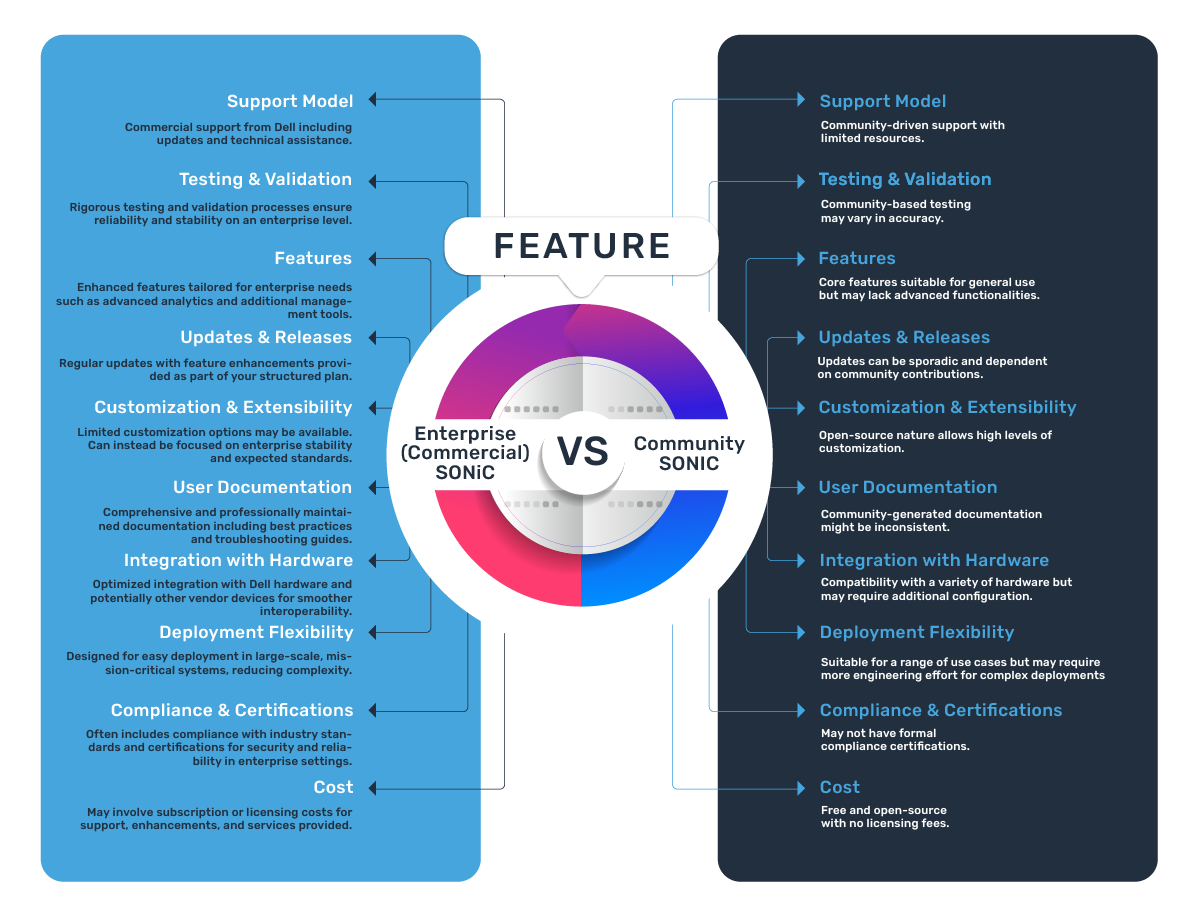
Answer: The former provides a commercially supported version of SONiC with enhanced testing, validation, and enterprise-ready functionalities. It incorporates critical features like advanced telemetry, AI fabric support, and management frameworks that assure operational efficiency in large-scale environments. The community’s free edition is more general in scope and focus. See table below for a deeper comparison.
| Feature/Aspect | Community SONiC | Enterprise (Commercial) SONiC |
|---|---|---|
| Support Model | Community-driven support with limited resources. | Commercial support from Dell including updates and technical assistance. |
| Testing and Validation | Community-based testing may vary in accuracy. | Rigorous testing and validation processes ensure reliability and stability on an enterprise level. |
| Features | Core features suitable for general use but may lack advanced functionalities. | Enhanced features tailored for enterprise needs such as advanced analytics and additional management tools. |
| Updates and Releases | Updates can be sporadic and dependent on community contributions. | Regular updates with feature enhancements provided as part of your structured plan. |
| Customization and Extensibility | Open-source nature allows high levels of customization. | Limited customization options may be available. Can instead be focused on enterprise stability and expected standards. |
| User Documentation | Community-generated documentation might be inconsistent. | Comprehensive and professionally maintained documentation including best practices and troubleshooting guides. |
| Integration with Hardware | Compatibility with a variety of hardware but may require additional configuration. | Optimized integration with Dell hardware and potentially other vendor devices for smoother interoperability. |
| Deployment Flexibility | Suitable for a range of use cases but may require more engineering effort for complex deployments | Designed for easy deployment in large-scale, mission-critical systems, reducing complexity. |
| Compliance and Certifications | May not have formal compliance certifications. | Often includes compliance with industry standards and certifications for security and reliability in enterprise settings. |
| Cost | Free and open-source with no licensing fees. | May involve subscription or licensing costs for support, enhancements, and services provided. |
Question: What advancements in the SONiC OS support the demands of modern applications such as AI and machine learning?
Answer: Recent versions of SONiC have integrated features that enhance performance for AI and machine learning.
Watch out for more information on this subject in a future article in this Series.
Question: How do organizations benefit from participating in the SONiC community?
Answer: Organizations that contribute to the SONiC community gain early access to new features and developments and can even influence the project's roadmap.
By establishing collaborations with other industry players, participating companies can align their networking solutions with other emerging cutting-edge technologies.
Recommended Resources for Reading:
- Sonic Foundation – Linux Foundation Project. (2023).
- What’s the Enterprise Impact of Microsoft’s Open-Sourced SONiC? (2023).
- SONiC, the Leading Open Source Network Operating System ... (2024).
- SONiC/Dell Enterprise Sonic Evaluation - Wikitech. (2023).
- Dell Technologies Delivers the Power of Open Source Networking ... (2020).
- Dell Adds Distribution of Open Source SONiC Network Operating System (2020).
- Connecting from Edge to Cloud, with Dell Enterprise SONiC. (2023).
- Is SONiC Right for You? 10 Reasons to Consider Before Deploying. (2024).